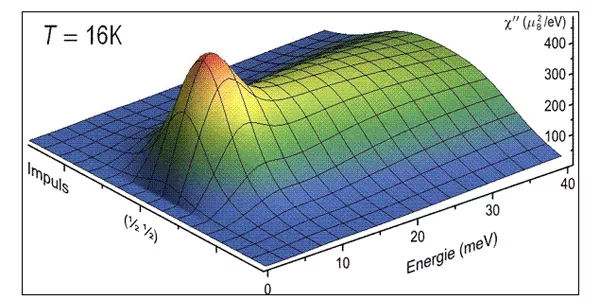
Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research have contributed to these findings with neutron measurements at the FRM II. They examined an iron arsenide at the three axis spectrometers PUMA and PANDA. The results were published online at Nature Physics.
Original publication:
Normal-state spin dynamics and temperature-dependent spin-resonance energy in optimally doped BaFe1.85Co0.15As2
D.S. Inosov, J.T. Park, P. Bourges, D.L. Sun, Y. Sidis, A. Schneidewind, K. Hradil, D. Haug, C.T. Lin, B. Keimer and V. Hinkov;
Nature Physics, Letters (2009)