The substance miltefosine (MF), originally developed as a remedy for breast cancer, works very well in the treatment of leishmaniasis. But MF has side effects on the human gastrointestinal tract. In addition, absorption into the body is reduced due to lipophilic barriers (membranes).
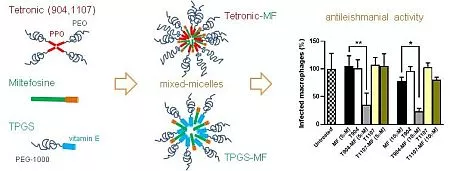
For their study, a research team from the University of Navarra in Pamplona (ISTUN Institute of Tropical Health and Department of Chemistry) and the University of Carlos III in Madrid (Department of Materials Science and Engineering, IQMAAB), together with scientists from the Jülich Centre for Neutron Science (JCNS) at the Garching outpost, used three different polymer-micellar systems based on polyethylene oxide (PEO). The aim of the study was to identify which drug carrier in combination with MF makes the drug more effective than the substance alone.
For this purpose, small-angle neutron scattering (KWS-2) was used at the Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Zentrum (MLZ) to analyse the structure of the polymer micelles in their compositions with MF over a wide temperature range. Together with the results of further investigations carried out in the laboratories in Pamplona and Madrid, the results allowed to characterize the morphology and composition of the polymer aggregates and to determine the exact position of MF in the drug carriers.
In biological studies on promastigotes and amastigotes – the extracellular and intracellular forms of the parasites, respectively – the activity of MF in the different formulations was then tested to identify the most promising “transporter”. The results show that MF works much better in all three combinations than on its own. This is particularly true when combined with a specific active ingredient carrier, the block copolymer T904.
Text: Forschungszentrum Jülich
Originalpublikation:
Joan Puig-Rigall, Celia Fernandez-Rubio, Javier Gonzalez-Benito, Judith E.Houston, Aurel Radulescu, Paul Nguewa, Gustavo Gonzalez-Gaitano: Structural Characterization by Scattering and Spectroscopic Methods and Biological Evaluation of Polymeric Micelles of Poloxamines and TPGS as Nanocarriers for Miltefosine Delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Volume 578, 30 March 2020, 119057; DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119057
Contact:
Dr. Aurel Radulescu
Jülich Centre for Neutron Science (JCNS) am Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Zentrum (MLZ)
Tel.: +49 89 289-10712
E-Mail: a.radulescu@fz-juelich.de
Presscontact:
Erhard Zeiss, Presse officer
Forschungszentrum Jülich
Tel.: 02461 61-1841
E-Mail: e.zeiss@fz-juelich.de